What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India
Union Territories are important parts of India’s federal administrative system. They are regions that are directly governed by the central government, unlike states, which have their own elected governments. Currently, India has eight Union Territories: Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, and Lakshadweep. The creation of these territories serves various purposes, including geographical, cultural, political, and welfare needs. Some areas were designated as Union Territories due to unique circumstances; for example, Puducherry was formerly a French colony, What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India.
Typically, Union Territories have a Lieutenant Governor appointed by the President of India. However, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, and Puducherry have a special status that allows them to have their own legislative assemblies and governments. The administrative structure of Union Territories differs from that of states because all legislative and executive powers are held by the central government, limiting their autonomy. Additionally, the cultural diversity of the residents in these territories contributes to India’s overall richness.
The history of Union Territories in India is linked to the formation of the Indian Union and its administrative needs. The concept was introduced in 1956 through the States Reorganisation Act to organize regions that were too small or unstable to become independent states.
The first group of Union Territories in India included the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Delhi, Manipur, Tripura, and Himachal Pradesh. Many of these areas later gained statehood, such as Manipur, Tripura, and Himachal Pradesh, while Delhi was designated as a Union Territory after 1956, What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India.
Puducherry, which was formerly a French colony, joined India in 1954 and was given Union Territory status in 1963. Similarly, Daman and Diu along with Goa were incorporated into India after gaining independence from Portuguese rule in 1961. Goa achieved statehood in 1987.
In 2019, the state of Jammu and Kashmir was divided into two Union Territories: Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh. Currently, India has a total of eight Union Territories: Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, and Lakshadweep.
The primary aim of establishing Union Territories was to allow direct administration by the central government to better address their administrative needs.
How are Union Territories administered
In India, the administration of Union Territories is primarily managed by the central government. Compared to states, UTs are subject to greater central control. Each UT has an administrator or lieutenant governor appointed by the President of India, who acts as the central government’s representative and oversees the administration of the territory.
Currently, India has eight Union Territories: Delhi, Puducherry, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu. Among these, Delhi, Puducherry, and Jammu and Kashmir have been granted partial statehood, allowing them to have their own legislative assemblies and elected governments. In contrast, other UTs do not have assemblies and are directly governed by the central government.
The process of creating special laws for Union Territories depends on the approval of the central government. For example, Delhi has been given the status of a National Capital Territory (NCT), which grants it some level of autonomy. In contrast, other Union Territories have more power concentrated in the hands of the administrator, while the role of the Chief Minister is limited.
Thus, the administration of Union Territories falls under a unitary structure where there is direct control from the central government. However, in certain specific situations, local autonomy is also provided, What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India.
What is the difference between Union Territory and state
There are several important differences between a state and a union territory in India. A state is an independent administrative unit that has its own elected government, which has the power to make laws and govern. Each state has a Chief Minister and a legislative assembly, and the Governor acts as its constitutional head. In contrast, a union territory is directly administered by the central government. Typically, there is an administrator or a lieutenant governor appointed by the President. Some union territories, like Delhi and Puducherry, may have their own legislative assemblies, but their powers are limited and often require approval from the central government.
According to the constitution, states have autonomy, while all powers in union territories lie with the central government. The relationship between states and the central government is federal, whereas the relationship between union territories and the central government is unitary, What is the difference between Union Territory and state.
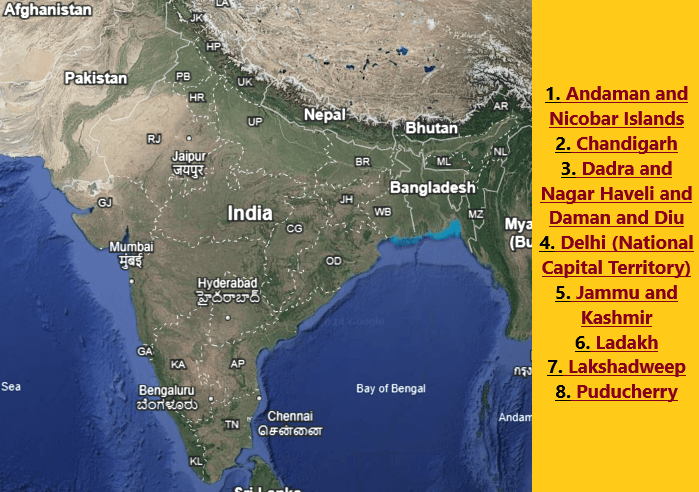
How many union territories are there in India
Currently, India has eight Union Territories. These are:
- Delhi (National Capital Territory of Delhi) – It was designated as a Union Territory on February 1, 1992, although it had been a special administrative region before that.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands – This territory was established as a Union Territory on November 1, 1956.
- Chandigarh – Chandigarh became a Union Territory on November 1, 1966, under the Punjab Reorganization Act.
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu – These two territories merged into one on January 26, 2020, forming a single Union Territory.
- Jammu and Kashmir – On October 31, 2019, Jammu and Kashmir was converted into a Union Territory after its special state status was revoked.
- Ladakh – Also established on October 31, 2019, Ladakh was created as a separate Union Territory from Jammu and Kashmir.
- Lakshadweep – This territory was designated as a Union Territory on November 1, 1956.
- Puducherry – After gaining independence from French rule on November 1, 1954, Puducherry was made a Union Territory.
The purpose of creating Union Territories in India is to manage regions that are economically, culturally, or geographically distinct from other states or have smaller populations that do not qualify for full statehood, What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India.
FAQs
What is union territory, What Union Territory means
Union Territory is a type of administrative division in India. These regions are directly governed by the central government. Unlike states, which have their own independent governments, Union Territories do not have the same level of autonomy. Some UTs, such as Delhi and Puducherry, have elected legislative assemblies, allowing them to have a degree of self-governance. However, other UTs are managed entirely by the central administration without any local legislative body.
Why union territories are formed
The formation of Union Territories in India was driven by various political and administrative reasons. These include the need to recognize unique cultural identities, address strategic importance, and provide special care for backward or tribal communities. For instance, Puducherry was established as a Union Territory due to its distinct cultural identity, while the Andaman and Nicobar Islands were designated as such because of their strategic significance.
Which union territory is the largest
Ladakh is the largest union territory in India, covering an area of about 59,146 square kilometers. It became a separate union territory on October 31, 2019, after being separated from Jammu and Kashmir. The unique geographical location and natural beauty of Ladakh make it an important region.
Which is the smallest union territory in india
Chandigarh is the smallest union territory in India, with an area of just 114 square kilometers. It is located at the borders of several states and was developed as a federal territory. Chandigarh is well-known for its urban planning and architecture, which were designed by the famous architect Le Corbusier, What is union territory, How many union territories are there in India.
